 |
SAI GM series hydrulic piston motor |


Crankshaft Design Radial Piston Motors
Model range: GM 05- GM9, Displacement (cc/r):59~12026, Torque (N.m): 235~47850
Rated pressure: 250 bar, Max. pressure: 350 bar, Power: 20~375 KW.
The main characteristics of this type of design are high mechanical efficiency, especially at start up, and high volumetric efficiency.
A number of features distinguish SAI Motors from other radial piston designs:
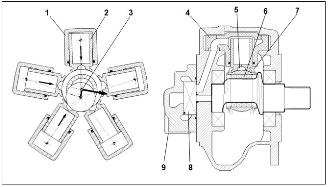
Displacement range (ml/rev.): 570 – 176720
Pivoting cylinder: the cylinder (1) remaining aligned with the eccentric of the crank (3), eliminates side loading between the cylinder and piston (2)The articulation of the cylinder-piston assembly is achieved with large diameter trunnions (4) ensuring low specific loads.Double piston support bearing: the pistons transmit their load to the shaft via a hydrostatic bearing (5) and a central roller bearing (6). The roller bearing eliminates the sliding velocity between the piston foot and the spherical piston support ring, reducing heat, friction, wearing and improving starting torque, low speed operation (reduced stick slip) and high speed operation. The hydrostatic bearing reduces metal-metal contact ensuring optimal lubrication and low friction.
Piston retaining rings (7) ensure the piston remains in contact with the shaft in all operating conditions, even during capitation.
Rotary axial distributor (8) ensures optimal distribution with short, large section ducts for reduced power-loss with high flows, and very high volumetric efficiency; extensive clearance recovery capability of the seals ensures optimal functionality throughout the motor lifetime and in conditions of thermal shock.
Interchangeable motor (9): a wide range of distributors are available with various pressure and flow control valves.
Sai GM Series Characteristics
GM Series Piston Hydraulic Motor are a result of the many years of experience gained with the preceding M, L and P Series Motors, and incorporate a number of design variations with respect to these series to in- crease the strength of the motor casings and the load capacity of the internal dynamic components. The result is a series of motors with high continuous power ratings, reduced internal loads and high mechanical and volumetric efficiency that contribute in reducing the amount of heat and therefore also the negative effects associated with it.
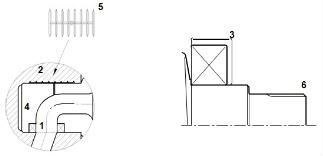
-
Radial injection cylinder feed (1) eliminates direct hydraulic axial loading of the motor casing.
-
Larger cylinder feed channels (1) for reduced power loss with high flows.
-
Stronger castings (2) and internal reinforcement ribbing: increased casing strength and stiffness for higher internal and external load capacity.
-
High load capacity bearings (3) for applications requiring high lifetime, high power/pressure, high external loads.
-
Larger cylinder trunnions (4) for increased strength and stiffness and reduced specific loads.
-
Cylinder trunnions with hydraulic balancing (5) to reduce friction, wearing and heat generation, enabling operation with higher powers and improved efficiency.
-
Compatibility with shafts (6), adaptors, flanges, distributors of the motors of the preceding series.
-
Reduced number of components for a more simple and reliable design.
-
Compatibility with non-polluting oils.
Technical Data of GAI GM Motor
Table of values (theoretical values, without efficiency and tolerances; values rounded)
GM05 motor |
GM05 90
|
GM05 110
|
GM05 130
|
GM05 150
|
GM05 170
|
|
Displacement cc/rev.
|
86
|
115
|
129
|
151
|
166
|
|
Rated torque Nm
|
343
|
458
|
513
|
600
|
660
|
|
Max. speed rpm
|
1000
|
900
|
900
|
900
|
800
|
|
Max. power KW(HP)
|
20(27)
|
20(27)
|
20(27)
|
20(27)
|
20(27)
|
|
GM1 motor
|
GM1 100
|
GM1 150
|
GM1 175
|
GM1 200
|
GM1 250
|
GM1 300
|
GM1 320
|
GM1 350
|
|
Displacement cc/rev.
|
99
|
154
|
172
|
201
|
243
|
290
|
314
|
340
|
|
Rated torque Nm
|
385
|
600
|
670
|
785
|
950
|
1130
|
1225
|
1060
|
|
Max. speed rpm
|
1000
|
1000
|
900
|
800
|
700
|
650
|
600
|
550
|
|
Max. power KW(HP)
|
48(65)
|
48(65)
|
48(65)
|
48(65)
|
48(65)
|
48(65)
|
48(65)
|
48(65)
|
|
GM2 motor
|
GM2 200
|
GM2 250
|
GM2 300
|
GM2 350
|
GM2 420
|
GM2 500
|
GM2 600
|
GM2 630
|
|
Displacement cc/rev.
|
192
|
251
|
304
|
347
|
425
|
493
|
565
|
623
|
|
Rated torque Nm
|
750
|
980
|
1188
|
1355
|
1658
|
1923
|
2208
|
2433
|
|
Max. speed rpm
|
800
|
800
|
750
|
750
|
750
|
700
|
700
|
650
|
|
Max. power KW(HP)
|
59(79)
|
59(79)
|
59(79)
|
59(79)
|
59(79)
|
59(79)
|
59(79)
|
59(79)
|
|
GM3 motor
|
GM3 500
|
GM3 600
|
GM3 700
|
GM3 800
|
GM3 900
|
GM3 1000
|
|
Displacement cc/rev.
|
486
|
595
|
690
|
792
|
873
|
987
|
|
Rated torque Nm
|
1895
|
2320
|
2700
|
3100
|
3400
|
3850
|
|
Max. speed rpm
|
600
|
575
|
500
|
500
|
400
|
350
|
|
Max. power KW(HP)
|
80(107)
|
80(107)
|
80(107)
|
80(107)
|
80(107)
|
80(107)
|
|
GM4 motor
|
GM4 600
|
GM4 800
|
GM4 900
|
GM4 1000
|
GM4 1100
|
GM4 1300
|
|
Displacement cc/rev.
|
616
|
793
|
904
|
1022
|
1116
|
1316
|
|
Rated torque Nm
|
2403
|
3100
|
3525
|
4000
|
4350
|
5125
|
|
Max. speed rpm
|
550
|
550
|
450
|
400
|
400
|
350
|
|
Max. power KW(HP)
|
100(134)
|
100(134)
|
100(134)
|
100(134)
|
100(134)
|
100(134)
|
|
GM5 motor
|
GM5 1000
|
GM5 1200
|
GM5 1300
|
GM5 1450
|
GM5 1600
|
GM5 1800
|
GM5 2000
|
|
Displacement cc/rev.
|
1039
|
1185
|
1340
|
1462
|
1634
|
1816
|
2007
|
|
Rated torque Nm
|
4050
|
4625
|
5225
|
5700
|
6350
|
7075
|
7825
|
|
Max. speed rpm
|
450
|
400
|
400
|
350
|
300
|
300
|
250
|
|
Max. power KW(HP)
|
120(160)
|
120(160)
|
120(160)
|
120(160)
|
120(160)
|
120(160)
|
120(160)
|
|
GM6 motor
|
GM6 1700
|
GM6 2100
|
GM6 2500
|
GM6 3000
|
|
Displacement cc/rev.
|
1690
|
2127
|
2513
|
3004
|
|
Rated torque Nm
|
6600
|
8300
|
9800
|
11875
|
|
Max. speed rpm
|
400
|
350
|
300
|
250
|
|
Max. power KW(HP)
|
170(228)
|
170(228)
|
170(228)
|
170(228)
|
PRESSURE RATINGS
All the motors are rated at a nominal continuous pressure rating of 3,650 psi. The continuous and average operating pressure, however, should be chosen in function of the required bearing lifetime (see bearing lifetime graphs). The peak operating pressures are given in the relative displacement tables. The motors may work at peak pressures for periods not exceeding 1% per minute, no more than 10 times per hour.
BACK-PRESSURE
The motors are capable of operating with high back-pressures with high efficiency, e.g. for series circuit applications.
The allowable pressures vary in function piston diameter and other factors. If the motors are required for an application with back pressure contact the technical department for further details.
CASE PRESSURE
Continuous case pressure: 15 psi, Peak case pressure: 75 psi. The case pressure is independent of the return line pressure.
For higher pressures (up to 350 psi) contact the technical department.
TORQUE
To obtain the theoretical output torque of a motor, multiply the specific torque (lb.ft/psi) given in the displacement tables by the pressure (psi). The graph below shows the output torque variation as the shaft rotates through 360°
STARTING TORQUE
Typical starting torque efficiencies are given in the performance graphs of the motors. The starting torque, how- ever, also depends on the starting position of the shaft.
LOW SPEED OPERATION
The motors are capable of operating at low speeds with a high degree of speed stability. The minimum stable speed depends on the displacement of the motor. In general the motors remain sensitive to flows of 6 in3/min + motor leak- age rate. Best results are obtained with 75-150 psi back- pressure and after the circuit has been completely purged of air by running it at 2/3 max speed for 5-10 mins.
The output torque does not fall off at very low speeds or at standstill.
NOISE LEVELS
The motors operate at lowest noise levels with a back-pres- sure of 75-150 psi, such as in closed circuits. Pressure lines and motor support structures can be efficient noise propagators or amplifiers. Pressure lines should preferably be made up of straight rigid lengths, flexible corners, firmly fixed to rigid supports at irregular intervals away from sheet paneling. Motors must be rigidly fixed to solid supports.
SILENT MOTORS
Motors can be supplied with special distributor that run nearly silently in a wide operating range.
Please contact technical department for further details.
VIBRATION
The motors can be supplied with a counterbalanced shaft to reduce vibrations at high speeds.
Please contact technical department for further details.
START-UP
Before connecting any tubes ensure that they are thoroughly cleaned, any excess material that could work loose should be removed and there should not be any oxidation of surfaces that come into contact with the oil.
Before starting work the motor casing must be filled with oil.
Before starting work the hydraulic circuit should be purged of air. This can be achieved by running the motor without load for 10-20 minutes, during which time checks should be made for leakages from connections.
During the first few hours of working under load checks should be made for leak- ages from connections and to ensure that all components remain firmly fixed to their supports.
All motors are factory tested and do not require to be run in.
To obtain details of this product range please contact us.



